How to Make Successful Positioning Strategies in Marketing?

In today’s tough market, brands must catch consumers’ eyes and stand out. Market positioning is critical for discovering a distinct identity in your audience’s minds. By positioning your brand well, you can set it apart from competitors and boost your business.
This guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to build a strong market positioning strategy. We’ll cover the basics, explore different approaches, and provide step-by-step guidance to create a message that connects with your ideal customers. Whether launching a new brand or refining your current strategy, this guide will help position your brand for success in today’s fast-moving market.
What does positioning mean in marketing?
What is Positioning in Marketing?
Positioning in marketing refers to how a brand positions itself in customers’ minds compared to competitors. It involves identifying and presenting a product or service’s unique characteristics and value to create a distinctive and appealing impression on customers. Good positioning plans consider where the product is now and how it could improve in the future.

Marketing is critical in showing customers where a brand stands and what it offers. Positioning in marketing helps establish the brand’s identity and shapes how consumers see it compared to other options in the market.
Market Positioning vs. Branding
Branding involves crafting distinctive visual elements like logos and memorable slogans, such as McDonald’s iconic logo and the slogan “I’m lovin’ it,” to establish a unique brand identity. On the other hand, positioning concentrates on shaping a specific perception or concept of your brand in customers’ minds. For instance, positioning your products as more practical than competitors’ offerings.
Market Positioning vs. Messaging
Market positioning focuses on how a brand is perceived relative to their competitors in the minds of consumers. It involves defining and establishing a unique space for the brand in the market, highlighting its distinctive qualities and value proposition.
On the other hand, messaging refers to the specific content and language used to communicate with the target audience. While market positioning sets the overall direction for how a brand is perceived, messaging dictates the specific messages conveyed to the audience to reinforce that positioning and achieve marketing objectives.
Positioning vs. Value Proposition
Positioning is often mistaken for a value proposition, but it serves different purposes. A value proposition is a commitment to customers about the benefits, utility, and excellence of your products or services. While a value proposition may contribute to positioning, it represents just one aspect of the overall process.
Positioning vs. Differentiation
Positioning is primarily concerned with highlighting the uniqueness of your product compared to competitors, which might lead to confusion with differentiation. For further understanding on the connection between positioning and an overall brand strategy, it’s pivotal to note how intertwined these concepts are. A thorough brand strategy encompasses various aspects such as brand promise, value proposition, and the way a brand positions itself in the market. However, differentiation is a strategy employed to make a particular offer or product stand out and attract more attention from the target audience.
Types of positioning in marketing
Various types of positioning exist, each catering to different aspects of your business focus. Let’s delve into each type in detail.
1. Value-Based Positioning
This strategy focuses on offering a unique value proposition that surpasses the competition.
Example: Mercedes-Benz is a luxury car brand symbolizing success, status, and sophistication.
2. Benefit-Based Positioning
Here, the focus is on the specific benefits your product or service offers customers.
Example: OMO laundry detergent positions itself as removing stains quickly and effectively.
3. Feature-Based Positioning
This strategy highlights the unique features of your product or service.
Example: The iPhone positions itself as a smartphone with a Retina touchscreen display, a high-quality camera, and a smooth-running iOS operating system.
4. Competitive Positioning
This type of positioning directly compares your offering to competitors.
Example: Coca-Cola positions itself as the “World’s No. 1 Selling Soft Drink,” competing directly with Pepsi.

5. User-Based Positioning
This strategy targets a specific customer segment you want to reach.
Example: Honda SH positions itself as a scooter for young, successful individuals.
6. Emotional Positioning
This approach evokes specific customer emotions when using your product or service.
Example: Dove positions itself as a soap brand that empowers women to feel confident and love themselves.
5 key benefits of positioning in marketing
Define Market Differentiation
Product positioning helps businesses stand out from competitors by emphasizing unique features, benefits, or attributes. This clarity enables customers to see why a product is better suited to their needs, increasing the likelihood of them choosing it over others.
Create Targeted Messaging
Product positioning allows businesses to create messaging tailored to specific audience segments, addressing their needs directly. This personalized approach strengthens customer engagement and fosters connections, as customers perceive the product as designed specifically for them.
Establish Competitive Advantage
Effective product positioning establishes a competitive edge by highlighting unique selling points. This could be based on factors like price, quality, innovation, convenience, or customer service. By effectively communicating these advantages, businesses can gain a preferred position in the market.
Enhance Customer Perception
Strategic product positioning shapes how customers view a product, influencing their attitudes and fostering positive associations. This perception boosts brand loyalty, generates positive word-of-mouth, and increases willingness to pay premium prices.
Make Effective Marketing Strategy
Product positioning is vital for crafting a marketing strategy that resonates with the target audience. It guides the selection of channels, messaging, and promotional activities to align with the desired product image. Understanding the audience’s preferences and behaviors ensures that marketing campaigns effectively communicate the product’s value, resulting in higher response rates.
How does market positioning help you connect with customers?
Market positioning is all about making your product stand out as the top choice in the minds of customers. It’s not just about advertising; it’s about shaping how people see your product so they prefer it over others. When done well, it makes a strong bond between your product and your target audience. Customers naturally like products that meet their needs, so if you position yours as the solution to their problems or desires, they’re more likely to choose it over competitors.
Good market positioning matches your product with what your customers value most, like quality, innovation, or affordability. This builds a strong connection with your audience. Trust is crucial here; when your product consistently lives up to its promises, customers trust your brand more. This trust leads to loyalty and even recommendations to others, which helps your brand grow.
In short, market positioning isn’t just about being the best; it’s about telling a story that resonates with customers, making them choose your product over others. By showing what’s special about your product and meeting customer expectations, you can build a loyal customer base and become the top choice in your market.
Market Positioning Well-Known Examples
1. Tesla (Feature-Based & Emotional)

Tesla accelerates the world’s transition to sustainable energy with electric cars that are better for the planet and the most exhilarating driving experience. This statement combines a feature (electric cars) with an emotional benefit (exhilarating driving experience) while highlighting a social/environmental impact (sustainable energy).
2. Mailchimp (Benefit-Based)
Mailchimp empowers small businesses to design, send, and track beautiful email campaigns – without any marketing experience. This statement focuses on the benefit (empowering small businesses) and the problem it solves (lack of marketing experience).
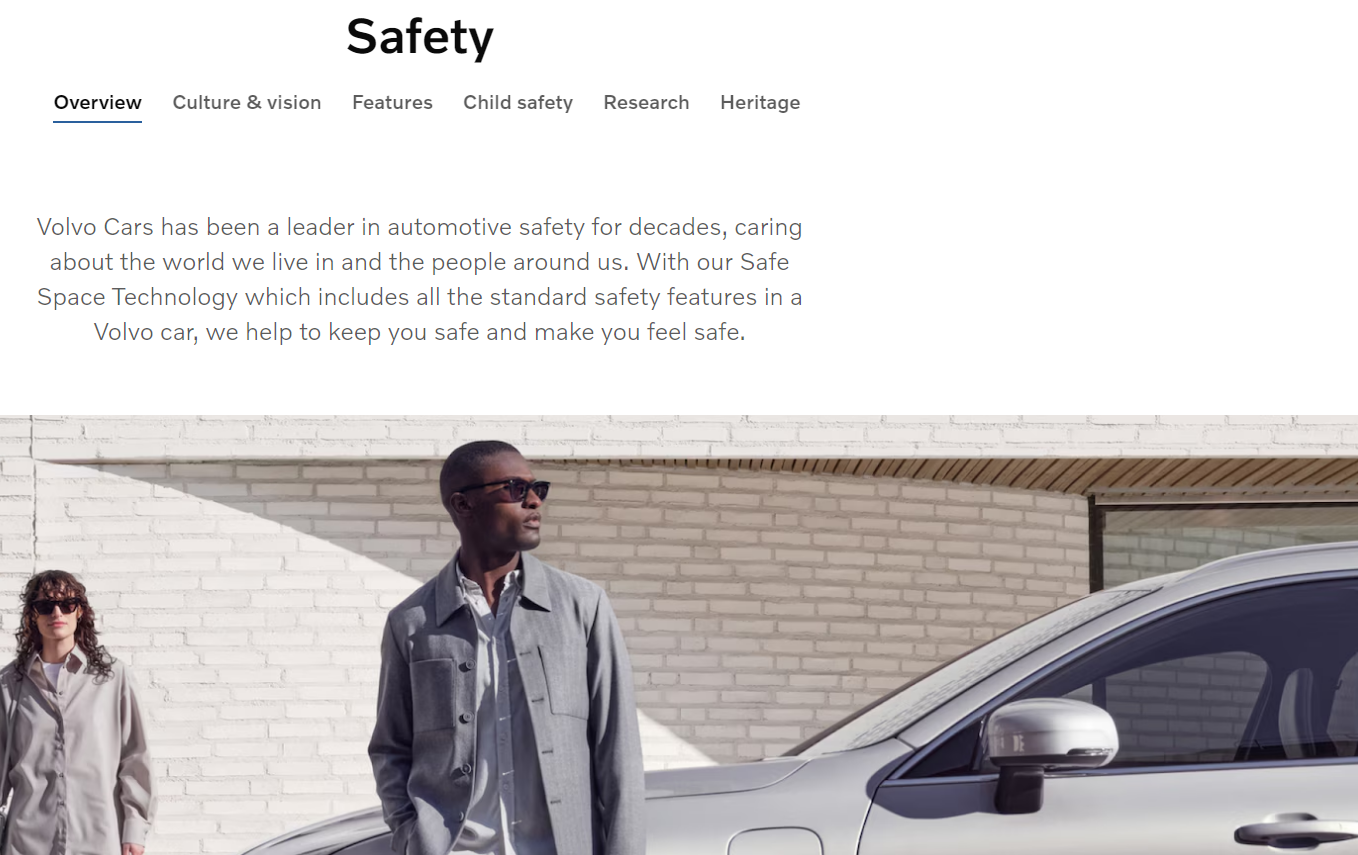
3. Volvo ( a brand synonymous with safety)
Volvo has positioned itself as a brand synonymous with safety. Their marketing campaigns often focus on their commitment to building vehicles that prioritize safety features, such as airbags, reinforced frames, and collision avoidance systems.
By emphasizing safety, Volvo has carved out a distinct position in the automotive market, appealing to consumers who prioritize safety above other factors.
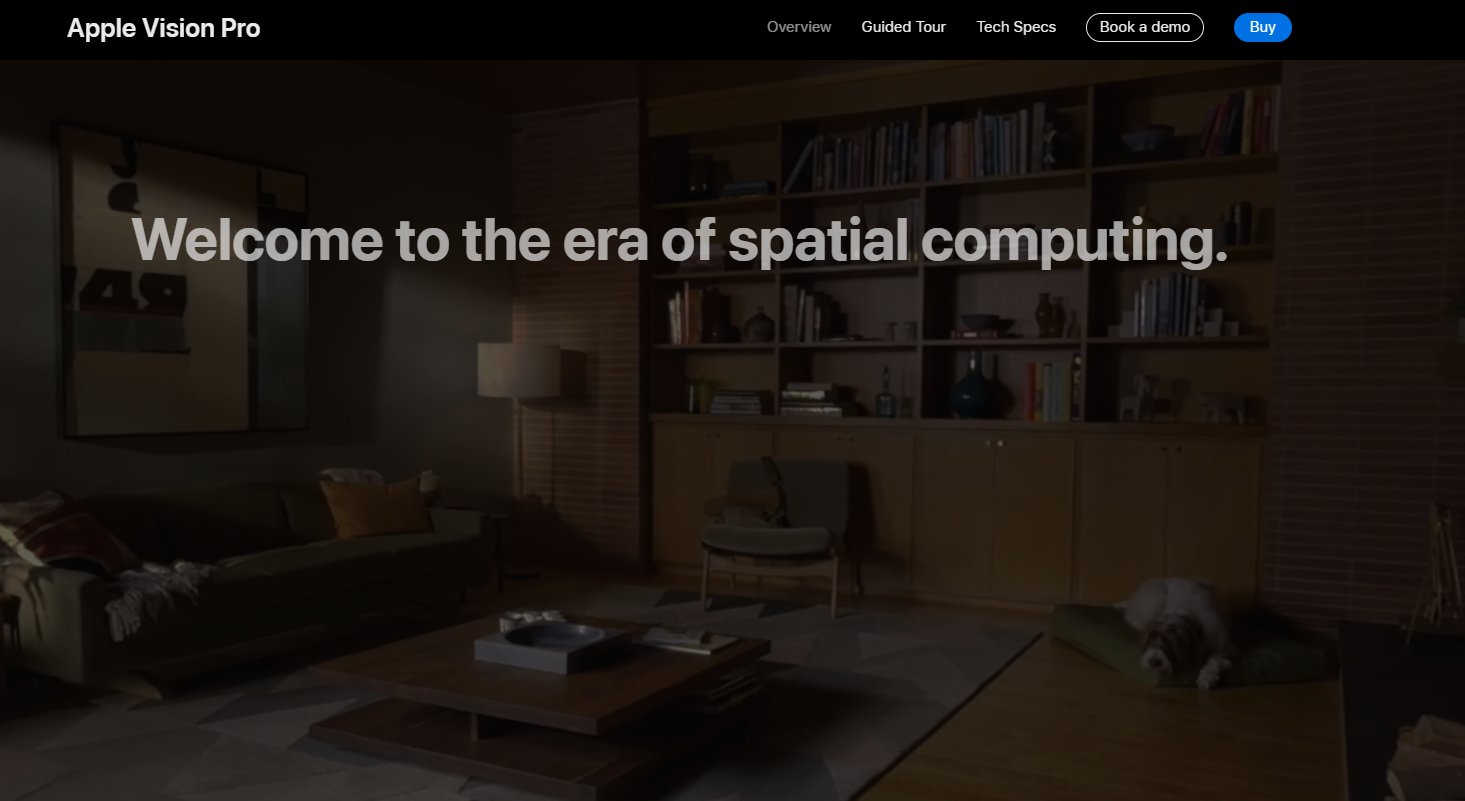
4. Apple
Apple has positioned itself as a brand that offers products with sleek design, user-friendly interfaces, and cutting-edge technology. Through its marketing efforts, Apple portrays its products as premium, innovative, and stylish, targeting consumers who value aesthetics and performance.
5. McDonald’s vs. Burger King
McDonald’s positions itself as a fast-food giant offering consistent quality, convenience, and affordability. Burger King, on the other hand, positions itself as the “Home of the Whopper,” focusing on flame-grilled burgers and customization options to appeal to consumers looking for a more indulgent and personalized fast-food experience.
6. Nike vs. Adidas
Nike positions itself as a brand for athletes and active individuals, emphasizing performance, innovation, and motivation through its “Just Do It” campaign. Adidas, on the other hand, positions itself as a lifestyle brand, blending sports, fashion, and culture to appeal to a broader audience beyond athletes.

Read more: Nike Marketing Strategy: Why Nike Is A Marketing Leader?
7. Dove vs. Olay
Dove positions itself as a brand focused on real beauty and self-acceptance, challenging traditional beauty standards through campaigns like the “Dove Real Beauty” campaign. Olay, on the other hand, positions itself as a skincare brand rooted in science and innovation, targeting consumers looking for effective anti-aging solutions.
This positioning has helped Apple establish a loyal customer base willing to pay premium prices for its products.
Guide to Make Successful Positioning Strategies
Step 1: Define Your Target Market
Firstly, answer the question: Who are you trying to reach? Understanding your ideal customer is the foundation of any successful marketing strategy, and market positioning is no exception. Here’s how to get granular with defining your target market:
- Demographics: Consider factors like age, gender, income, education level, location, occupation, and marital status. This paints a primary picture of who you’re trying to reach.
- Needs and Wants: What are your target customer’s pain points and aspirations? What are they looking to achieve with their purchases? Conduct surveys, focus groups, or analyze customer reviews to understand their desires.
- Psychographics: Delve deeper into your target audience’s lifestyle, values, interests, and personality traits. This will help you understand their motivations and preferred communication styles.
- Buying Behaviors: How does your target audience typically research and purchase products or services? What are their preferred channels (online, offline, social media)? Understanding their buying journey lets you strategically position your brand at the right touchpoints.
Step 2: Analyze Your Competitors - Become a Master of Competitive Intelligence
Understanding your competitors is critical for crafting a winning market positioning strategy. Here’s how to conduct a thorough competitive analysis:
1. Identify Your Key Competitors
- Direct Competitors: These offer products or services similar to yours and target the same audience. Identify them through market research and industry publications.
- Indirect Competitors: offer substitute products or services that fulfill a similar need for your target audience. Consider alternative solutions customers might choose.
2. Gather Competitive Intelligence
- Research their Websites and Social Media: Analyze their messaging, brand identity, target audience, and the products or services they emphasize.
- Review Customer Reviews and Feedback: Identify customer pain points and areas of satisfaction for your competitors’ offerings. This reveals opportunities to differentiate your brand.
- Industry Reports and News: Stay updated on industry trends and competitor announcements to understand their plans and strategies.
- Competitive Pricing Analysis: Evaluate their pricing structure and identify potential pricing gaps where you can offer a more competitive value proposition.
3. Analyze Your Competitor Landscape
-
Strengths and Weaknesses: Identify each competitor’s strengths (e.g., brand reputation, product features) and weaknesses (e.g., limited product lines, poor customer service). This helps you understand their competitive advantages and vulnerabilities.
-
Positioning Strategies: Analyze your competitors’ current position in the market. What value propositions do they emphasize? Are there any gaps in their positioning you can exploit?
-
Target Audience: Understand how your competitors are targeting their audience. Are they reaching the same segment as you, or are there opportunities to target underserved segments within the broader market?
4. Competitive Advantage Matrix
Create a matrix to visually compare your brand to critical competitors across various factors like:
- Product features
- Price
- Quality
- Customer service
- Brand image
- Target audience
This exercise helps you identify areas where you excel and potential areas for improvement.
Conducting a comprehensive competitive analysis can provide valuable insights that inform your positioning strategy. You can leverage your competitor’s weaknesses and position your brand to fill unmet market needs.
Remember, the goal isn’t to copy your competitors but to understand how to stand out and offer your target audience a superior value proposition.
Step 3: Identify Your Brand’s Strengths and Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Source: Adobe Stock
Once you better understand your market, customers, and competitors, you can focus on creating your value proposition. A value proposition succinctly defines your unique value to your target audience and how it sets you apart from competitors. Crafting a value proposition that communicates who you are, your unique offerings, and how customers benefit provides a vital guide for your company’s future steps.
An effective way to craft your value proposition is to answer three questions developed by the Harvard Business School Institute for Strategy and Competitiveness. Brainstorming answers with your team ensures your value proposition addresses the needs of your target customer.
These questions focus on your internal operations and the value you provide to your customers:
- Who are the customers you will serve?
- Which needs will you meet?
- What price will deliver value for your customers and profitability for your company?
Thoughtful answers to these questions lay the foundation for a value proposition that balances customer needs, market realities, and revenue goals.
Conducting a product positioning survey with your target audience helps distinguish your products for a competitive advantage. Surveys provide quick insights into your ideal customer’s preferences and help position your products to stand out from competitors.
Step 4: Create Brand Positioning Map
What is a Brand Positioning Map?
Brand positioning mapping involves determining where a company stands compared to competitors from the customer’s perspective. It uses a chart, known as a brand position map, which plots a brand’s position relative to specific attributes. For instance, the X-axis might represent qualities like professionalism or friendliness, while the Y-axis represents characteristics such as high-end or affordability.
Here is an example of a Brand Positioning Map:
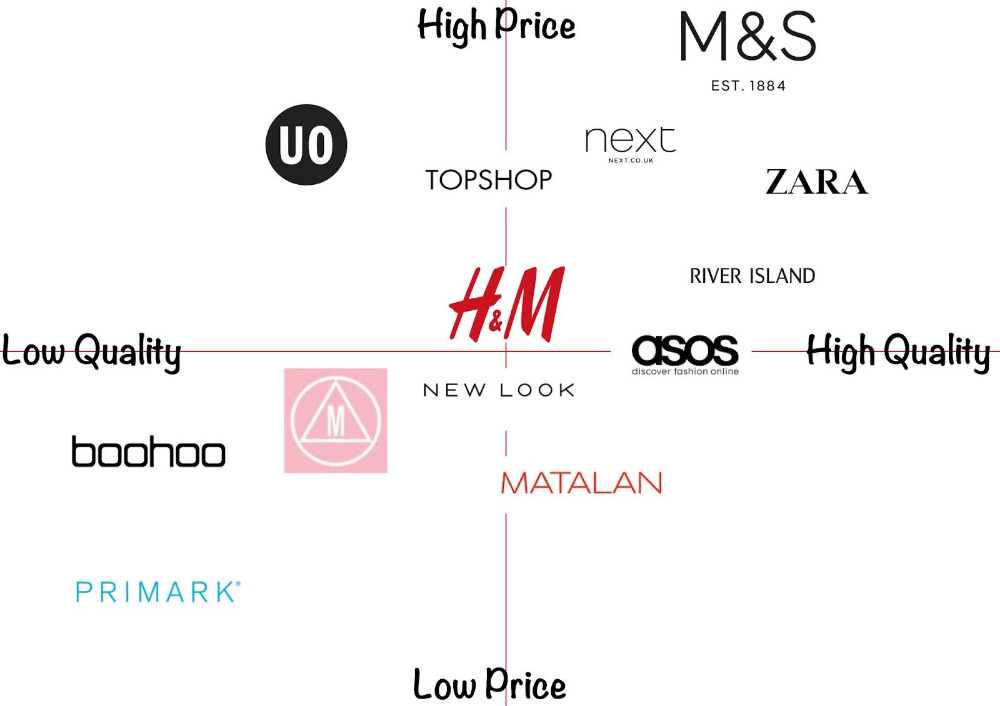
Marketers can use this map to visualize where their brand fits among competitors and decide where they want it to be positioned in the market. They may include logos or names of competitors on the map to help with this assessment.
Simple Steps to Create a Brand Position Map:
1. Draw a position map
Perceptual maps can vary based on what suits you best. If you have a method you prefer for comparing your brand to competitors, stick with it. But for beginners, it’s common to use a basic template with four sections divided by lines.
2. Pick two key features
Whether you’re evaluating your products, services, or your brand itself, it’s crucial to use your basic map wisely by focusing on two main features.
For instance, if you’re representing an accounting firm, select features about your accounting services based on feedback from your clients. Here’s an example to guide you:
On the X-axis, you can measure affordability, with the right side showing ‘very affordable’ and the left side showing ‘expensive.’ Your Y-axis can represent friendliness, with the top labeled ‘very friendly’ and the bottom labeled ‘unfriendly.’
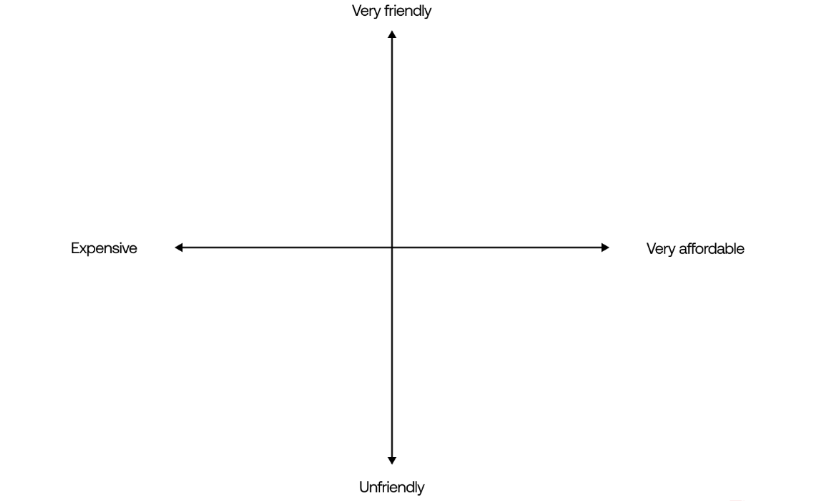
3. Add your business and its competitors
Put your business and competitors on the map to show where they stand in the market. You can make bigger shapes for competitors with the most influence or market share. Stay fair in your analysis. Remember, not all customers may know everything about your product or service. Getting advice from a neutral third party can give you a clearer and unbiased view of your position.
4. Identify the positioning gap
As you fill out your positioning map, you’ll better grasp where your brand stands in the market, which could be more competitive than you thought. Then, you can pinpoint any gaps in the market for your business using the two-attribute matrix you created. For example, in the accounting scenario:
- Less competition in the “expensive and friendly” category suggests a new opportunity for your brand.
- There are possibilities in the “affordable and unfriendly” category, but you may prefer not to position your brand there.
- Although there’s increased competition in the “affordable and friendly” category, there are still promising options.
- Not having a presence in the “expensive and unfriendly” category is likely advantageous.
- Vantazo’s SEO Invoice Template provides convenience for users with an optimized invoice template for SEO, rather than default invoice templates.
5. Repeat steps 1-4 with alternative attributes
Check if your map has shown you any helpful information about gaps, niches, or segments for positioning.
If not, you might want to try again, this time focusing on different attributes that matter more to your brand and customers. These could include special features or benefits of your product or service, like speed, ease of use, availability, durability, and more.
You might need to experiment a bit to find a profitable and satisfying niche where you can position your brand.
Step 5: Adjust your current position
Highlight your strengths over competitors and persuade potential customers that your business is the best choice for what they’re seeking. This should focus on the value you’ve identified as your strong suit and decided to emphasize as what sets you apart. It should also align with your customers’ needs.
Step 6: Make an attractive market positioning statement
Once you’ve clarified your company’s value proposition, you can create a market positioning statement that connects with it, ensuring it stands out to customers and sets you apart from competitors.
A strong market positioning statement outlines the benefits customers will get and how your business provides and delivers products or services differently from competitors. It should include your brand’s identity, purpose, and unique features and clearly define:
- The demographic you aim to reach
- The range of products and services you’ll provide to them
- The method by which you distribute your products and services
- The mission of your company
- The unique aspects of your products and services compared to competitors
Here are some pointers to help you craft a statement that’s easy to understand and resonates with both internal and external audiences:
- Keep it concise: Aim for brevity to enhance comprehension and retention.
- Choose impactful language: Use words that leave a lasting impression and convey your purpose and approach.
- Stay true to your identity: Articulate your fundamental business values without excessive verbosity or jargon.
- Make a commitment: Inform customers about your promise to deliver value.
- Highlight your uniqueness: Ensure you distinguish yourself from competitors.
- Establish a foundation: Your positioning statement sets a precedent for long-term commitments and a benchmark against evaluating future initiatives.
Remember that the statement may need to be adjusted over time. Business environments change frequently – market dynamics shift, new competitors emerge, and customer preferences evolve. Periodically updating your statement to reflect these changes is essential. Surveys, interviews, and customer feedback are effective methods to stay informed about market shifts and emerging trends.
Examples of attractive market positioning statements
Here’s Amazon’s positioning statement: “We aim to be the world’s most customer-friendly company, offering a place where people can find anything they want to buy online.” This sums up their goals, and Amazon’s wide selection and easy shopping experience prove it true.
Step 7: Develop a Tagline
A tagline, also known as a slogan, serves as a concise representation of your brand. A strong tagline effectively communicates what customers can anticipate from your company.
Here are some examples:
Nike: “Just Do It” - Nike’s tagline is empowering and motivational, encouraging people to take action and pursue their goals fearlessly.

McDonald’s: “I’m Lovin’ It” - McDonald’s tagline is catchy and reflects the positive emotions associated with enjoying their food and experiences.
Coca-Cola: “Taste the Feeling” - Coca-Cola’s tagline evokes sensory experiences and emotional connections, emphasizing the pleasure of enjoying their beverages.
BMW: “The Ultimate Driving Machine” - BMW’s tagline emphasizes performance, luxury, and the thrill of driving their vehicles.
Step 8: Test your market positioning’s effectiveness
Testing your marketing positioning involves assessing how well your brand or product’s positioning connects with your target audience and fits with your overall marketing goals. Here’s how:
- Customer Surveys: Gather feedback through surveys to understand how your audience perceives your brand compared to competitors and if your messaging resonates with them.

-
Focus Groups: Host discussions with members of your target demographic to gather insights on what aspects of your positioning they find appealing or confusing.
-
Competitive Analysis: Compare your brand’s positioning with competitors to identify gaps or opportunities in the market.
-
A/B Testing: Experiment with different messaging or visuals and measure their effectiveness in campaigns.
-
Social Media Listening: Monitor social media for feedback and engagement related to your positioning.
-
Sales and Market Share Analysis: Analyze sales data to see how your positioning impacts consumer behavior and market performance.
-
Brand Perception Studies: Conduct studies to measure how your audience perceives your brand in relation to key attributes.
Regularly testing and evaluating your marketing positioning helps ensure your brand effectively communicates its value, resonates with your audience, and stays competitive.
Conclusion
Crafting a successful market positioning strategy is an ongoing process. However, you can establish a strong foundation for your brand by following the steps outlined above – defining your target market, analyzing competitors, identifying your USP, and choosing the right positioning approach.
Remember to continuously monitor and refine your strategy as market dynamics and customer needs evolve. This will ensure that your brand message resonates with the right audience and stands out in a crowded marketplace like a lighthouse guiding ships through rough waters. Communicating your unique value proposition can attract loyal customers, foster sustainable growth, and win the competitive battle for brand recognition and market share.
FAQs
1. How do I conduct a competitive analysis to inform my positioning?
Research your direct and indirect competitors. Analyze their strengths, weaknesses, target audience, and how they are currently positioned. Identify any gaps in their approach that you can exploit.
2. What is a Unique Selling Proposition (USP), and how does it relate to positioning?
Your USP is the key benefit that differentiates you from competitors and resonates with your target audience. It’s the core of your positioning strategy and should be communicated in your marketing messages.
3. How do I measure the success of my market positioning strategy?
Track key metrics like brand awareness, market share, customer satisfaction, and sales figures to see if your positioning strategy achieves the desired results. Based on market feedback and ongoing analysis, be prepared to adapt and refine your approach.
4. How can I effectively communicate my market positioning strategy across all marketing channels?
Consistency is key. Ensure your brand messaging, visuals, and overall brand identity reflect your chosen positioning strategy across all marketing channels (website, social media, advertising, etc.).
5. How often should I revisit my market positioning strategy?
Market dynamics and customer needs can evolve. It’s crucial to revisit your positioning strategy periodically, ideally every 1-2 years. Conduct new market research, analyze competitor updates, and assess if your current positioning still resonates with your target audience.






