8 Effective Ways to Fix 400 Bad Request Error
Vinh Jacker | 07-21-2023

If you spend a lot of time surfing the internet, chances are you’ve come across this “400 Bad Request Error” message at some point. It’s frustrating and confusing, and it can make you feel like you’re stuck in a never-ending loop.
In this article, we’ve got you covered with 8 tips to help you handle this issue. So let’s dive in and get your web browsing back on track!
What is a 400 Bad Request Error?
A 400 Bad Request error is an HTTP status code describing an error caused by an invalid request. This error occurs when their web browser or application cannot send an understandable request to the server. When the server receives an invalid or malformed request from the client, it cannot fulfill the request.
The error message is often displayed on the screen as “400 Bad Request” or “HTTP Error 400.” Incorrect syntax in the request, missing or invalid parameters, or issues with the web server are the common causes of this error.
The 400 Bad Request Error message may look different depending on your browser. In Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge, the browsers return an intimidating message, but the error can be a blank page on Safari or Firefox.
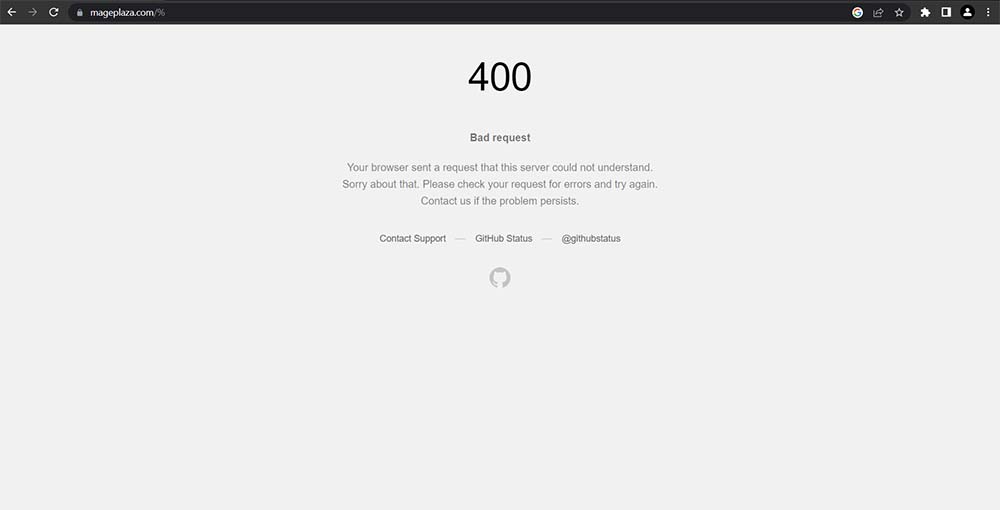
Why do we need to fix 400 Bad Request errors?
There are several reasons why we should fix 400 Bad Request errors. Here are some:
-
Poor user experience: 400 Bad Request error prevents users from accessing the content they need on a website or application. Thus, it can negatively impact the user experience.
-
Bad search engine rankings: A high number of 400 Bad Request errors can negatively impact a website’s search engine rankings. The reason is that search engines may interpret these errors as a sign of poor website quality.
-
Degraded website performance: A website with a high number of 400 Bad Request errors can put additional load on the server. Since the server has to generate an error message for each failed request, it can slow down the website’s response time.
What causes the 400 Bad Request error?
Below are some common causes that lead to the 400 Bad Request error:
-
Invalid or incorrect URL: If the URL in the request is incorrect or malformed, the server may not be able to process the request and return a 400 error. The malformed URL may contain invalid characters such as {, }, [, or ]. An incorrectly encoded URL may contain incorrectly used ASCII characters, such as double percentage characters.
-
Invalid syntax: Incorrect or malformed syntax in the request message is the most typical reason for a 400 Bad Request error. These can contain parameters, headers, or missing or inaccurate data.
-
Large file size: On each website, there is a file upload limit. Any attempt to upload a file that exceeds this limit is deemed a bad request. That’s when the HTTP 400 error status code happens.
-
Server error: This error can also occur due to problems on the server side. A 400 status code, for example, could indicate a general server failure, a server bug, or other undefined temporary issues.
-
DNS cache: When the website you want to visit has changed domain names or web hosts, the DNS cache data in your operating system might be invalid. That’s when 400 Bad Request error messages show up.

Site Audit Services
Mageplaza offers FREE site health check (15hrs) to help you identify any website flaws & weaknesses and fix them before they start costing you a fortune.
Explore MoreHow to fix the 400 Bad Request error?
Check the URL and parameters
This common culprit of a 400 Bad Request error can be fixed by verifying that the URL is properly formatted. When typing the URL manually into the browser, we may inadvertently include unwanted characters.
Ensure the domain name and specific page you’re attempting to access are accurately typed. Consider special symbols such as a hyphen (-) or percentage character (%) if the URL comprises a directory path, file name, or query string.
Additionally, ensure that the domain is separated by forward slashes. If the URL contains special characters, they must be correctly encoded and legal URL characters.
If you want to detect incorrect characters automatically in the URL, consider using this online URL encoder/decoder. This tool will greatly help when you want to enter a less error-prone URL.
Clear cookies and cache
To improve the browsing experience, data, and files are saved by browser cookies and cache on the user’s side. A website needs to properly run these types of files, such as HTML, JavaScript, media files (images, videos, audio), etc.
Cookies save the user’s session history and settings, allowing for customized browsing. And yet, cookies can expire after some time. In another case, some browser extensions can also change your cookies, leading to a 400 Bad Request error.
To fix this, clearing cookies and cache is a must. Here’s how you will do that:
- Click on the three-dotted icon on the right-hand corner in Google Chrome and select More Tools > Clear Browsing Data from the popup menu.
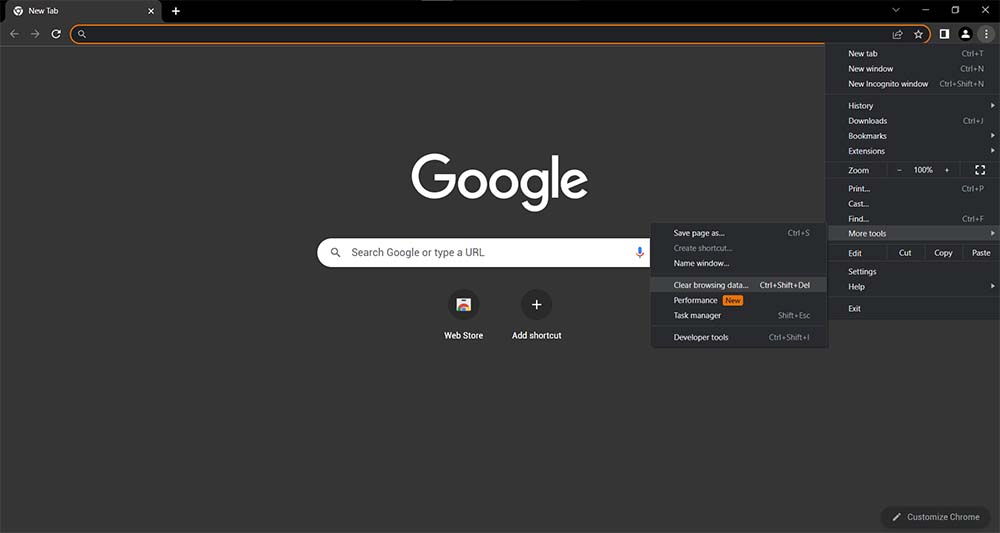
-
The Clear browsing data window will show up. From this window, select the Cached images and files option, then click the Clear data button to delete the browser cache.
-
You may also use the Time range dropdown to delete recent files for a certain time range. We recommend selecting the All Time option and removing all locally stored data to ensure that all possibly corrupted files are deleted.
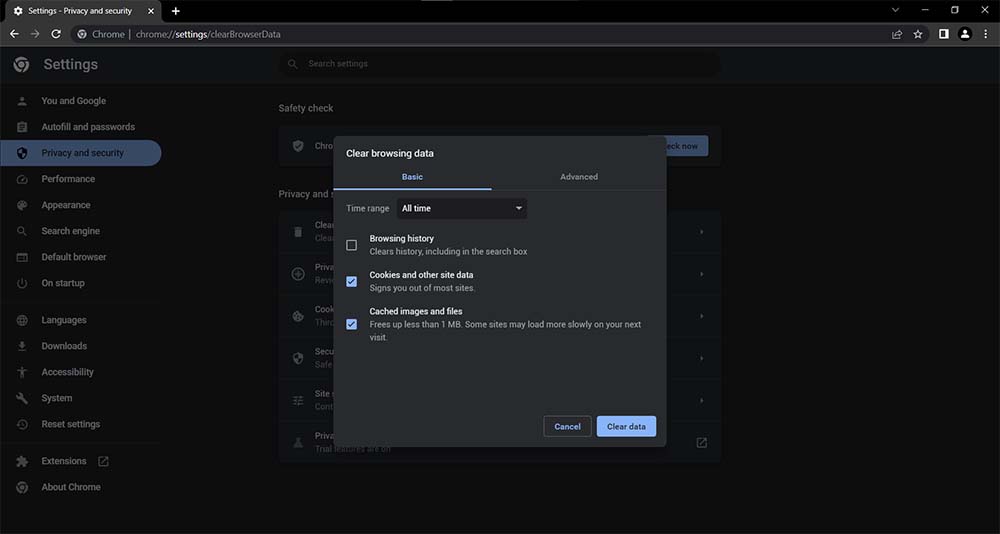
Remember that emptying the cache and cookies in your browser changes the settings and logs you out of websites you’ve visited. It will also take longer to load websites since the browser will need to download previously saved content from the cache.
Disable browser extensions
Browser extensions can also cause a 400 Bad Request error. This is because these extensions may interfere with the request submitted to the web server, causing the web server to perceive the request as invalid.
If so, you should temporarily deactivate all the extensions before connecting to the website again. To do this, take the following steps: On Google Chrome’s top right corner, select the three-dotted menu. Then choose Extensions -> Manage Extensions.

- You can turn off all extensions separately by clicking on the switch button.

Reload the website. If it loads normally, one of the extensions is the culprit behind the 400 Bad Request error.
Once you know the cause of the 400 Bad Request error, you need to identify the exact extension causing it. You will uncover the culprit by turning off the extensions one at a time and reloading the web page after each one. Continue to disable the extension by clicking the Remove button.
Flush DNS Cache
Corrupted or out-of-date local DNS lookup data also cause a 400 Bad Request error.
This is because when you visit a website for the first time, the system performs a DNS lookup. This process is to find the nameservers and IP addresses associated with the domain name.
Your operating system then caches the IP addresses of the web servers. As a result, the system can speed up the next visit by reducing the DNS lookup process.
However, an outdated or corrupted DNS cache can be the leading cause of the 400 Bad Request error. You may want to clear the DNS cache if this is your case. No matter which operating system you are using, this practice will save you from technical problems and data leaks.
Check the file size
Uploading a file larger than the server’s limit may trigger the 400 Bad Request error. Because each site typically has a file upload limit, ensure the file you want to upload falls within that restriction.
If the website does not specify a file limit, you can test the limit by uploading a small file. If it works, you should downsize the file you want to upload.
You should keep in mind that file compression can degrade file quality. It can make the content of a PDF or image blurry and unreadable. Checking the file’s quality after compression is a good way to ensure whether the file’s acceptable to upload or not.
There are plenty of free online compression resources that you can tap into. HiPDF for PDF files and UniConverter for audio and video files are two excellent tools that you should try.
Try opening other websites
If you got a 400 Bad Request error when viewing one particular website, try opening other websites to see if the problem still exists. If the error persists, the issue may be with your computer or networking equipment rather than the website you’re attempting to access.
Contact the site owner
If you have tried all of the above methods and still cannot fix the 400 Bad Request error, there’s a possibility that this error lies on the site owner’s side.
In this case, you should contact the site owner by filling out a contact form on the contact page. Another way is to inform them via email addresses and social media accounts. The owner may have been notified about the issue and working on it.
Restart your computer and other equipment
The last resort is to restart your computer and other hardware, such as modem and router.

Because it clears the RAM (Random Access Memory), restarting the computer often addresses various problems, including the 400 Bad Request error. Additionally, it can clear the temporary caches created when you open and close programs.
Conclusion
If you face a 400 Bad Request error, numerous methods exist to resolve the problem. It is important to remember that the error’s root cause may not always be apparent and that more advanced troubleshooting steps may be necessary in some cases. However, approaching the problem logically can boost your chances of discovering a solution.
Overall, by staying focused and following the tips provided in this blog, you may adequately troubleshoot and fix the 400 Bad Request errors. You can get back to using the internet with confidence and ease.






