Mobile Commerce: Key Elements, Benefits and Ways to Improve

It is a fact that in recent years, smartphones have changed from communications devices to life’s necessities. The process was accelerated by high-speed WiFi and the Covid pandemic. Grocery shopping, doctor visits, and banking all went online.
Mobile commerce has become one field that we simply cannot put our phones down for. Thanks to the convenience of smartphones, we can now easily purchase, sell, and pay through our phones. And such ease has resulted in the surge of E-commerce transactions from $1.9 trillion in 2021 to $2.2 trillion in 2023, with more than $3 billion anticipated by 2027.
To marketers, this is a very crucial opportunity. In this guide, we’re going to take a look at just what mCommerce entails, its advantages, and how you can exploit it for your business.

What Is Mobile Commerce?
Mobile commerce, also called m-commerce, refers to wireless electronic commerce. This means using handheld devices with wireless connectivity, such as mobile phones and tablets, to buy or sell goods online, conduct online banking, or pay bills.
Key Takeaways
- M-Commerce refers to buying or selling with the help of cell phones or any device with a similar function.
- It allows customers to conduct transactions anywhere they can reach access to a wireless Internet provider.
- Increased as security issues were overcome.
- Companies like Apple and Google have launched their own m-commerce services.
M-Commerce vs. E-Commerce
E-commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods and services via the Internet, in general. It can be done through a laptop, a computer, a smartphone, or even a tablet computer. With this, users who use computers traditionally needed to have a location with access to the Internet.
On the other hand, m-commerce refers to transactions made through a smartphone or mobile device. The users of m-commerce can make any transaction anywhere in the presence of a wireless Internet provider in an area.
Transactions via m-commerce are done within just a few clicks. On the contrary, e-commerce is done via a tablet, laptop, or desktop and may need more time and searching of a company’s website.
The Future of Mobile Commerce
According to a December 2022 Morning Consult poll, more than 60% of US adults say mobile shopping is a must-have for online shopping convenience.
Mobile commerce trend means retailers and online marketplaces must create well-designed, easy-to-use experiences for both their mobile websites and apps. Studies in June 2024 showed that US mobile phone users would, on average, spend just 3 hours and 15 minutes (3:15) a day on their phones in 2024.
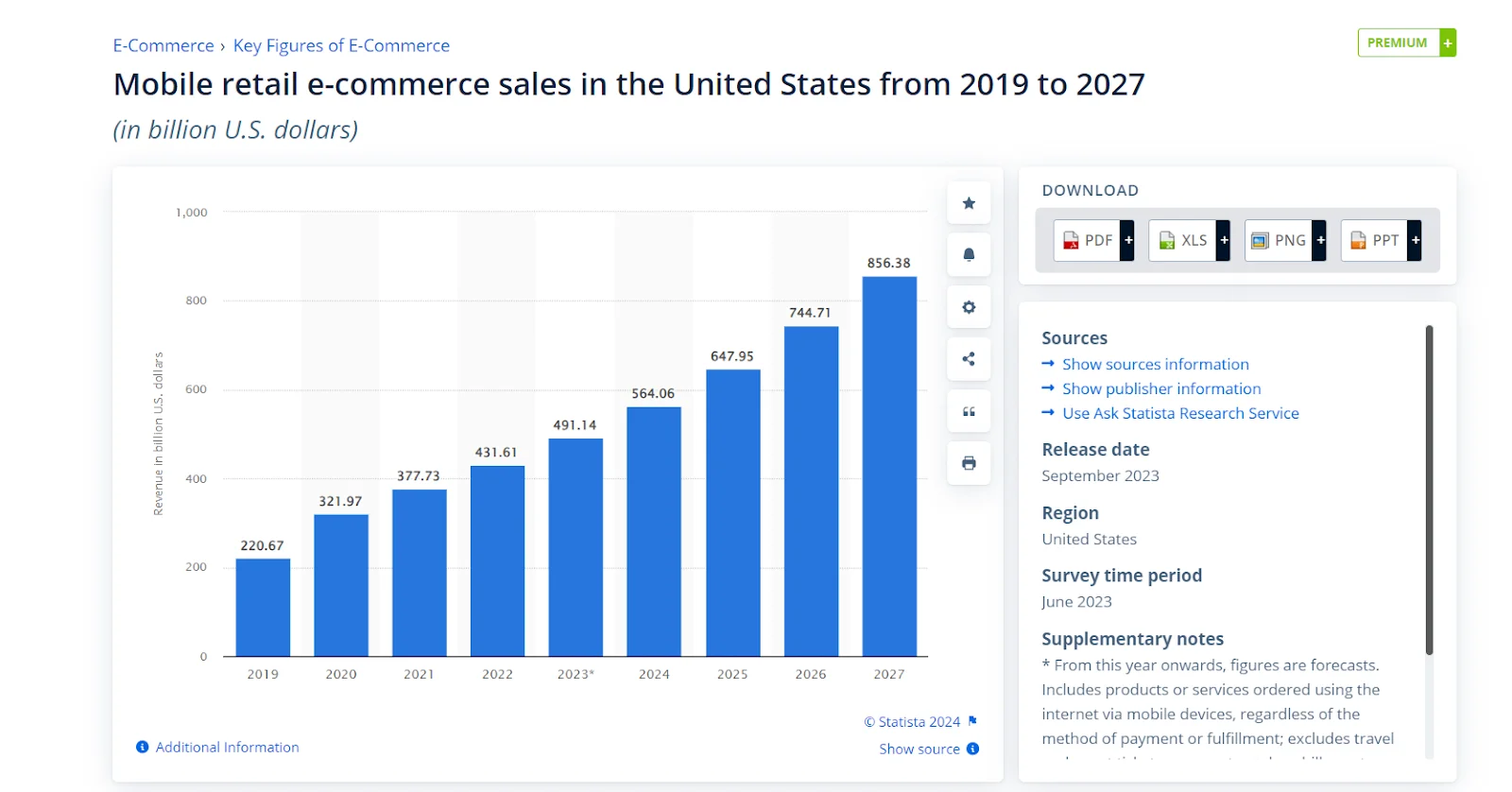
As more smartphones are used, the sale of m-commerce increases. In 2027, US retail m-commerce sales will reach $856.38 billion, nearly double the revenue in 2022.
Benefits of Mobile Commerce
The categories of devices that can perform m-commerce has expanded. Digital wallets, for instance, Apple Pay, allow customers to pay for purchases in the store without the hassle of swiping a card. Social media companies began adding “buy buttons” on their mobile platforms in the “mid” to late-2010s, including Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), Pinterest, and Instagram. This also allowed customers to purchase items from other retailers without leaving the social media sites.
Mobile commerce apps use location tracking via GPS or nearby customer service to help customers find items in stores. Personalized shopping experiences connect retailers to their clientele in ways asserted via “consumer” interviews.
Ways to Improve Mobile Commerce
Web pages with fast load times will probably place more sales as consumers tend to be impatient and transformed into instant gratifiers. Mobile checkouts should make it easy for consumers to enter their payment information. Or, use their mobile wallets and reduce the entry of payment information to avoid human error while facilitating smoother checkouts.
Key Elements of Mobile Commerce
M-Commerce has changed retail by providing easy, on-the-go shopping experiences. Let’s look at the key elements that make it impactful:
1. Mobile Shopping
Consumers can easily enter and shop from eCommerce stores using mobile-friendly websites or apps. These platforms have easy-to-use interfaces, so it’s simple to see products, compare prices, and make purchases from their phones.
2. Mobile Payments
Retailers have even enhanced the shopping experience for consumers with many payment options. Consumers can pay via online banking, mobile wallets like Apple Pay, PayPal, or Google Pay, or conduct contactless payments via virtual debit or credit cards at in-store POS systems. Having this purchase flexibility increases overall conversion rates or the shopping experience as a whole.

3. Location-Based Services
Retailers on mobile commerce stores can offer unique deals or promotions based on a consumers location through GPS-enabled smart phones. Deploying these unique strategies allows businesses to present brands to their customers at the right time and space. This enhance the positive shopping experience, and boost sales for the retailer.
4. Mobile Advertising
You may be aware that create location-led personalized ads that seek to meet user needs based on user mobile activity or characteristics. Mobile advertising allows retailers to implement personalized ad campaigns that are targeted as per mobile-use, increasing the relevance and total campaign engagements through ads distributed via promotions targeted for individuals.
5. Mobile Ticketing
Consumers can buy and store electronic tickets for events, travel, or entertainment directly on their mobile devices. Such a possibility of not using the physical tickets enriches the customer user experience. Thanks to most of the difficulties will be removed, thus the user will benefit from the convenience and accessibility.
Altogether, these key components establish an environment in which mobile commerce functions as a vehicle of customer satisfaction and propels retail growth.
Mobile Commerce Videos and Marketing

Essentially mobile apps that portray a product with video for specifications are more likely to generate revenue.
In reality, a financial online trading broker who sends video links showing its new mobile trading application likely will acquire new clients. That’s easy to understand! Who does not want to buy a product with extremely clear in both visuals and benefits, right?
How Mobile Commerce Can Help Boost the Bottom Line
Mobile shopping experiences give customers ways to interact with brands more than they otherwise would, driving e-commerce sales.
State that since Americans check their phones hundreds of times per day, mobile e-commerce is an area ripe for investment.
Mobile omnichannel shopping
By omnichannel shopping, customers browse items on one device and make a purchase on another. Persistent shopping carts and geolocation services ensure customers who come to the ecommerce platform from another device can access items that were previously added to a cart and show the same personalized content across devices.
It is also among the main sources of footfall inside the store and vice-versa. According to Think With Google, 59% of shoppers visit a store just to see or touch a product even when they plan to buy it online.
Location-based marketing

It is a way of marketing that involves offering services, notifications, and advertisements on digital platforms depending on user device location.
This may be an ad for a concert coming to their city or new home listings in their area. Geolocation creates content based on a circumstance the user is currently experiencing.
Here’s precisely how it works:
- Geofencing: Establish virtual boundaries around a physical location-a store, shopping mall, or arena. When a mobile device enters or exits these boundaries, the mobile commerce marketing tactic starts! They’ll receive notifications or offers.
- Beacon technology: It’s used to use in a small area. Bluetooth-enabled devices positioned in public areas to transmit signals into nearby mobile phones. Businesses send messages, promotions, and other content to users’ smartphones whenever they are in proximity to a beacon.
- Location-based notifications: It ‘s about sending SMS or push notifications regarding events, information, discounts, or really anything the business owners want. Notifications of upcoming events or special deals onto user devices near their location.
- Local search: Through check-in options on social media, e-commerce businesses can encourage users to do so and reward them with discounts or loyalty points, among others.
Improved customer engagement
A mobile companion app or responsive mobile website can help increase the frequency of customer interactions with the brand. Send timely push notifications alerting shoppers of promotions, new arrivals, abandoned carts, and special events. Use in-app messaging for live chat to support mobile shoppers.
Bring augmented reality into play, enabling users to virtually “try before they buy”; see what furniture items may look and feel like in their space, or how a pair of glasses or shade of eyeshadow would look on them.

To get more customer attention, check out our post here.
Mobile Commerce Challenges to Keep In Mind
When building for mobile devices, remember that they have limited computing power and may have varying signal strength. Because of these and other factors, mobile commerce may not always be the ideal choice.
Security and privacy concerns
Mobile devices expose one to vulnerabilities in ways which a desktop computer cannot.
For example, customers connect their smartphones to open public Wi-Fi, which might intercept their data. The lost or stolen mobile devices could expose an owner’s personal information.
To secure the customer’s personal data on their mobile devices, follow these steps:
-
Strong authentication: Make them create good, unique passwords, and give them the option for two-factor authentication. Also, allow them to log out remotely when their device has been stolen.
-
Encryption: This shall ensure that sensitive payment information is encrypted in transition, and when it’s stored.
-
App permissions: One should try to avoid asking for permissions not needed, like location tracking, unless the core function requires your app to do so. Turn off those permissions whenever the app is not in use.
-
Security updates: Regular patching of a mobile application or website prevents cyber attackers from using unknown vulnerabilities.
Speed and Performance Ensuring
Keeping that in mind, mobile commerce applications and sites are also more likely to fail on a mobile due to factors beyond your contro. Because their processing power, memory, and storage are weaker compared to desktops. This makes the rendering of intensive web pages really much slower.
High-resolution images and rich media content showcase products in their best light. However, these assets can lead to longer page-load times on mobile. Apps that rely on location data, such as ridesharing apps, can contribute to latency when GPS signals are poor.
Read more: 13 Mobile Marketing Tips for Optimal Website Performance
App store guidelines
Application developers should be bound by the guidelines provided by both the Apple App Store and the Google Play Store for approval of the app to further continue their existence in these stores.
Breaking any of these may lead to the removal or rejection of an app, among other sanctions.
-
Guidelines of App Stores: Each store has its own set of rules and policies concerning the content, functionality, design, and user experience of the apps.
-
Privacy and data collection: Clearly provide information on how user data is going to be collected, shared, and secured. Follow the applicable regulations concerning data protection.
-
In-app purchase: Stores have rules regarding how an app processes payments, subscription models, and price transparency.
-
User experience: Do not use aggressive advertising, pop-ups, and spam notifications that can trigger negative reviews from users.
-
Age ratings: If your app requires age restrictions, make sure to set the appropriate age ratings and apply restrictions in content accordingly.
-
Metadata of app stores: These include the actual description, title, and keywords of an app.
Mobile commerce is one of the fastest-evolving industries and transforms the way people shop and interact with brands and products. Today, the focus will fall on how best the overall customer experience can be optimized through mobile-first design, smooth checkout processes, and real-time personalized recommendations in order to optimize user engagement and accelerate user decision-making.
Wrap Up
Mobile commerce is, indeed, a great opportunity for both merchants and consumers. It’s a win-win situation, allowing shoppers to have more convenience while shopping and boosting sales for store owners. The future of m-commerce is also bright with the fact that new technology only develop for the better. So, what are you waiting for? Let’s take advantage of mobile commerce right away!





