Ecommerce Security: Common Threats and Tips to Protect Your Store

A robust eCommerce security strategy is essential for the success of any online business. Threats can arise from various sources, and studies show that 88% of professional hackers can breach an organization within just 12 hours, as reported by DataProt. Given the looming risk of unauthorized access to your company’s data, safeguarding against potential reputational damage and business disruptions is paramount.
While many ecommerce companies employ basic security measures, it’s challenging to stay vigilant when hackers continually adapt their attack methods. Relying solely on the hope that existing solutions suffice is insufficient.
To effectively protect your data, it’s crucial to understand and implement proactive security measures for your online store. Refer to our guide below for insights into safeguarding your ecommerce company’s data.
What is eCommerce security?
In essence, eCommerce security encompasses a set of universally accepted principles aimed at ensuring secure online shopping experiences. These guidelines safeguard both businesses selling products online and customers sharing personal information for purchases.
Understanding various aspects of e-commerce security is crucial when establishing necessary protocols for your online store. These include:
-
Verification of identities through authentication to confirm the legitimacy of both buyers and sellers.
-
Protection of customer data, particularly from unauthorized access by third parties, known as privacy.
-
Maintenance of data integrity, ensuring that information remains unaltered or tampered with.
-
Adherence to non-repudiation principles, legally enforcing commitments made during transactions.
Importance of eCommerce security

Safeguarding Customer Data
Ecommerce platforms collect and store sensitive customer information such as bank details, credit card numbers, addresses, and personal details. Failure to secure this data can result in identity theft, financial losses, and harm to individuals. Additionally, the loss of customer data can damage a business’s reputation, leading to potential loss of trust and subsequent revenue.
Preventing Financial Loss
Insecure ecommerce platforms are highly susceptible to cyber attacks, with numerous malicious acts occurring daily aimed at hacking websites. Statistics show approximately 30,000 websites are hacked worldwide on a daily basis. Any breach can result in financial losses for both the business and its customers, making robust security measures imperative.
Upholding Reputation
A breach in security can significantly damage the reputation of an ecommerce business. It is crucial to secure the platform to maintain customer trust. Customers typically prefer websites they trust, and a breach can lead to a loss of trust, impacting revenue. Preserving reputation through effective security measures is essential for sustained success.
Gaining Competitive Advantage
In the competitive landscape of ecommerce, demonstrating a strong commitment to security can provide a competitive edge, especially for smaller businesses competing against established brands. Focusing on security practices and offering customers a safe shopping experience can differentiate a business and attract more clientele, thus enhancing its competitive position.
Common eCommerce security issues to avoid
A security breach occurs when unauthorized third parties gain access to buyers’ identities and financial details, posing a significant threat to online stores. Here are some common methods cybercriminals use to attack online businesses:
Spam

Spam typically entails sending mass emails, often using tactics like urgent “action required” messages. Additionally, your website’s comment section and contact forms serve as open avenues for spammers to insert infected links, potentially compromising databases. This not only undermines website security but also damages the credibility of your eCommerce business.
Furthermore, hosting spam comments on your site could lead to penalties from Google, adversely affecting your site’s SEO ranking and discouraging user engagement with your content.
Financial Fraud
While the theft of bank account credentials has long been recognized as a primary threat in eCommerce fraud, online criminals are becoming increasingly innovative. Here are various financial fraud schemes that online businesses may encounter:
-
Payment Fraud: Criminals typically utilize stolen credit card information, email addresses, user accounts, or IP addresses to pose as legitimate customers. This can result in fraudulent purchases, the creation of fictitious accounts, or manipulation of website traffic.
-
Clean Fraud: This form of fraud involves deceiving cardholders into making transactions on counterfeit websites or intercepting messages exchanged during transactions. This allows fraudsters to obtain copies of the personal data submitted. Alternatively, credit card details may be purchased from illicit sources on the dark web.
-
Affiliate Fraud: Many businesses engage in affiliate marketing programs to drive revenue. Cybercriminals exploit these programs by generating malicious traffic and fraudulent sign-ups, deceiving businesses into paying them affiliate commissions.
-
Triangulation Fraud: This scheme involves a three-step process of enticing buyers, gathering their personal information, and exploiting it for illegal purposes. Fraudsters create fake websites advertising non-existent inexpensive products. When customers submit their data, it falls into the hands of the perpetrators automatically.
Malware
Malware (malicious software) is a program or code intended to cause harm to computers, networks, or servers. It is commonly distributed through links to malicious websites or email attachments.
Once a user interacts with the link or opens the file containing malware, the malicious code is activated and begins carrying out its intended actions. These actions may include stealing sensitive data, establishing backdoor access, or spying on the user’s online activities.
Malware comes in various forms, including:
-
Adware (advertising-supported software): Unwanted advertisements that can degrade device performance by consuming system resources, such as RAM.
-
Trojan horse: Malware disguised as legitimate files or attachments, often leading to unexpected changes in computer settings.
-
Fileless malware: Utilizes legitimate programs to infect systems without leaving detectable traces, making it challenging to identify and remove.
-
Ransomware: Prevents users from accessing their system or files until a ransom is paid to regain access.
-
Rootkits: Designed to evade detection by antivirus software and other security tools, allowing attackers to clandestinely monitor and access victims’ computers.
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks rely on personal interaction between the scammer and the victim, constituting a significant aspect of cyber threats. According to a report, over 30% of successful data breaches result from such attacks.
Instead of exploiting technological vulnerabilities, social engineering attacks manipulate human emotions and behaviors to gain access to sensitive information, capitalizing on the victim’s trust in the attacker.
Detecting social engineering attacks can involve identifying suspicious attachments, poor grammar or formatting in messages, or generic email greetings.
Three common forms of these attacks are:
-
Phishing: Involves mimicking legitimate websites or applications to steal credentials via email, text, or phone calls.
-
Quid Pro Quo: Scammers offer assistance or information to gain access to devices or inject malware.
-
Pretexting: Attackers pose as authorities or coworkers to coax victims into revealing personal data or completing tasks.
Bots

Bots are software programs designed to perform tasks with speed and efficiency beyond human capability. While bots can serve legitimate purposes, cybercriminals also use them to mimic human behavior for financial gain and malicious activities, infiltrating company computers and servers.
According to a survey by Kount, one in four businesses experienced losses of up to $500,000 due to bot attacks in 2020.
Additionally, bots can exploit vulnerabilities in identity and access management (IAM) systems. IAM systems are digital frameworks that authenticate users’ identities and regulate their access to resources, particularly cloud identity and access management solutions that address scalability and security in cloud environments. Weak IAM systems are often unable to differentiate between legitimate human users and malicious bots, making them susceptible to exploitation.
Brute Force Tactics
Brute force tactics involve systematically guessing credentials to access an eCommerce site’s admin panel. Hackers employ specialized software to attempt various combinations of letters, numbers, and symbols until they find the correct password.
Upon successfully brute-forcing their way into a website, hackers gain access to valuable database information. This includes sensitive data such as customer identities, bank account details, and other confidential information, which can be exploited for profit.
In 2016, the Alibaba-owned eCommerce platform Taobao fell victim to a significant brute force attack, compromising the data of 21 million users. Hackers exploited a database of 99 million passwords and usernames to gain unauthorized access to accounts.
DoS and DDoS Attacks
The main objective of both DoS (Denial of Service) and DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks is to render a website inaccessible by flooding it with requests from anonymous IP addresses.
One key distinction between DoS and DDoS attacks lies in the number of connections utilized. While DoS attacks involve a single connection, DDoS attacks utilize multiple internet connections, making it harder to pinpoint their source as they originate from various locations.
Business owners must prioritize eCommerce security, especially during peak periods like Black Friday or Cyber Monday sales, to safeguard against such attacks.
E-skimming
E-skimming, also known as a Magecart attack, is a hacking method that employs concealed malicious code. This code clandestinely captures customers’ transaction data as they finalize purchases on a compromised website.
Subsequently, hackers utilize the stolen information to execute illicit transactions. Financial details of online shoppers, including full names, card verification codes, and expiration dates, are then traded on the dark web.
In 2019, a significant e-skimming attack targeted the website of a well-known American department store, Macy’s. Attackers implanted a Magecart script on both the homepage and the checkout page of the site.
11 Ways to Strengthen Your eCommerce Store’s Security
1. Train your Team for Phishing Awareness
A phishing attack is a target where hackers target victims via SMS or Emails using impersonation. The source of the Email may seem legitimate but the motive is to steal personal information or credentials.
Today, phishing attacks are responsible for 36% of all security breaches. They aren’t just aimed at companies and management but are targeted towards individuals working in organizations. Your employees may ultimately make the mistake of palling prey to these hackers and unknowingly leak sensitive organizational information.

To avoid this, make security training a part of your organizational culture. This will require you to implement change management and make security training an important component of employee training rather than an afterthought.
You’ll have to create phishing campaigns, make employees aware of the type of phishing attacks, how to prevent them, report them, enforce real-time reporting, etc. You can use Sophos to provide phish threat training to your employees.
2. Take Better Control of Your Passwords
The practice of following good credential hygiene starts at home. Despite the threat to securities, companies often overlook the basics of password security.
Cultivate a practice of never ever repeating a password for any of the internal systems that you use — For either public-facing logins or administrative accounts. Set up schedules for updating passwords and create unique passwords for every site.
This sounds difficult but fortunately, you have a lot of password management tools like Dashlane to make this process easy.
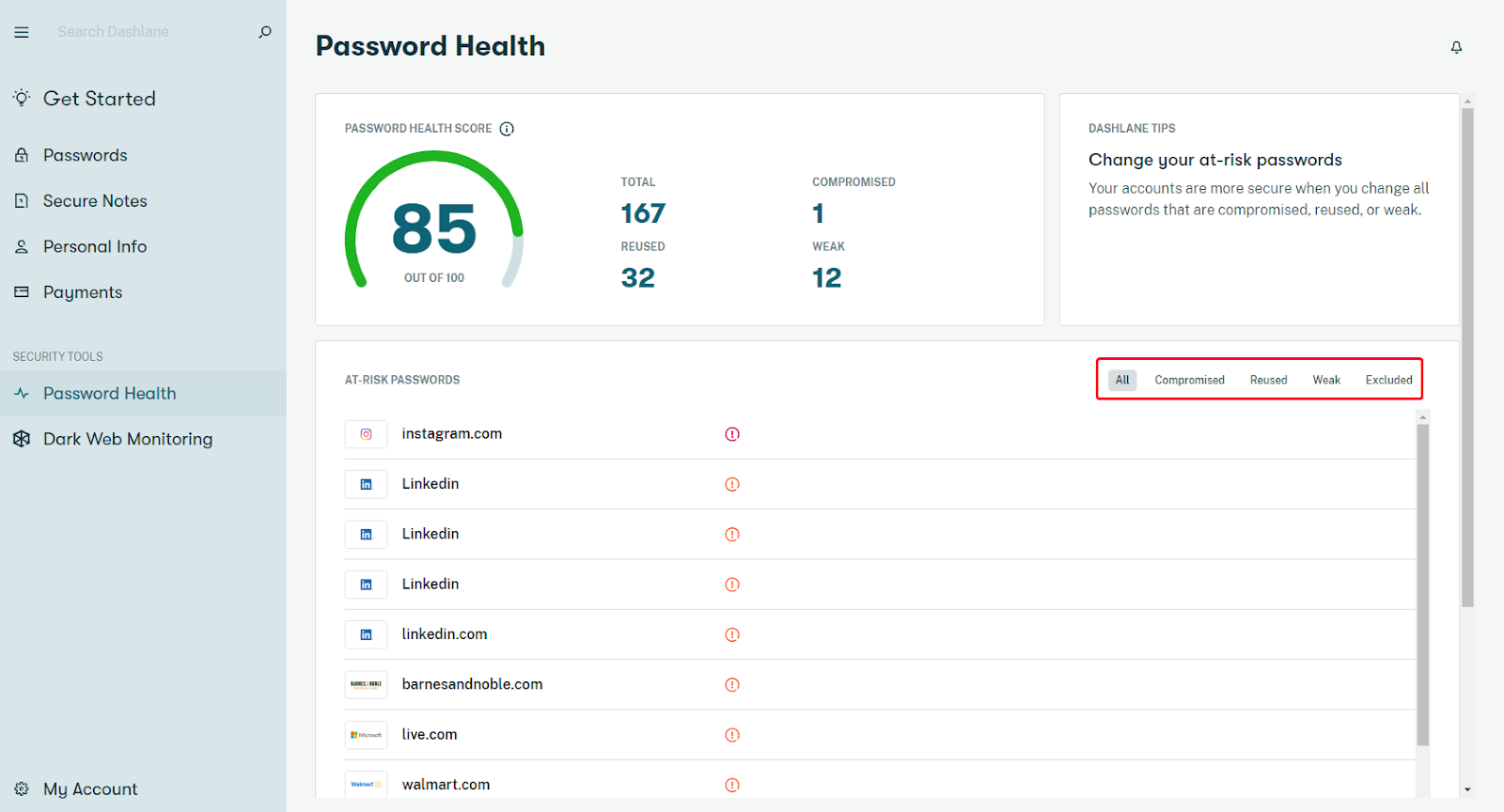
These tools sync all passwords under a single device and protect your data. Some of the best password managers not only help you generate strong passwords from an encrypted vault but also ensure secure autofill and seamless access across devices.
3. Set up two-factor authentication
While you cannot set your customers’ passwords, you can take a security measure by enforcing two-factor authentication.
According to Microsoft, a multi-layered authentication process can block over 99% of cyber-attacks!
Two-factor authentication doesn’t just require the user to input a username and password. You send an extra code that is sent as an email or an SMS on their provided phone number.
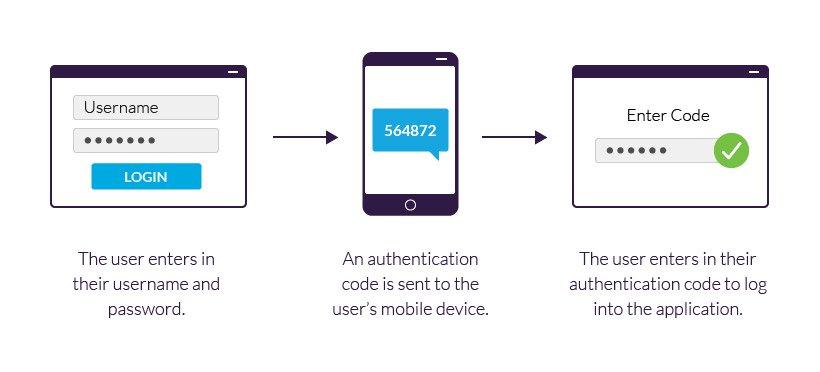
This would ensure that only the user is accessing the service even if their username and password are at risk. You can use MFA authentication tools like Duo MFA to enable multi-factor authentication in your logins.
4. Encrypt your Entire Store
As an eCommerce store, it is a must for you to get an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) Certificate that links a key to transactions on different paths on a network. It is one of the primary requirements for eCommerce stores under PCI (Payment Card Industry) compliance.
In simple terms, a properly installed SSL certificate helps you protect and secure your site data by encrypting all the information submitted on your site. This makes it difficult for hackers to read and interpret your data.
The certificate doesn’t just protect your data but also enables HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) on your site. Instead of a standard HTTP, the extra S of ‘Secure’ encrypts, connects, and adds a padlock icon next to your address bar. It will build trust amongst your consumers and show them that your site is protected and secure to use.
5. Don’t Trust Native CMS Security
CMS platforms are common hacking targets. Their open-source nature makes them vulnerable and nobody really pays attention to the finding and patching the CMS security vulnerabilities on time.
Since a CMS has numerous plugins and integrations, they are also often exposed to cross-site scripting and SQL Injection.
There’s a lack of accountability in these open-source CMS and you cannot trust it to be always secure. Some of the steps you can take to mitigate CMS security risks are:
- A solution you must follow is to regularly update your CMS to avoid attacks. Choose a vendor that takes care of security updates.
- Look for top-recommended security plugins in case you’re using an open-source CMS to fill the gaps where native security was thin.
- Sanitize user inputs to prevent injection attacks. Utilize typed and parameterized database queries in programming languages.
- Change default usernames like ‘admin’
- Enable a Firewall
- Schedule regular black box pentests to simulate real-world attacks to identify and patch vulnerabilities traditional methods might miss
6. Take Extra Steps to Help Customer Security
Passwords are the most standard access key that your customers will have. And customers are often inadvertently using the same password at multiple places for easy remembrance.
The problem with poor credential hygiene from the customer’s end is it makes it easy for hackers to crack passwords and breach security.
In this case, your customers can end up being your weakest link. Like I mentioned before, you don’t have any control over what passwords they keep. But you can take measures for your customers to follow the best practices for ensuring security. Some must-haves login security measures that you can take are:
- Enforce a rule for customers to build a password that’s a mix of capital letters, numbers, and, special characters to increase the complexity and strengthen their passwords.
- Have a minimum password length
- Block Dictionary Words, Usernames, and Compromised Passwords
- Use an on-screen password strength meter
- Remind them to update and change their passwords every few months.
- Limit login attempts
- Use a Google reCAPTCHA to make logins secure
You can utilize Mageplaza’s Magento 2 Security extension that helps you prevent unauthorized access to hackers and tighten the security for logins.
7. Ensure Frequent Backups
Imagine if the hacker didn’t just breach your security but also destroyed and wiped your data.
It would be a disaster, wouldn’t it? You didn’t just lose the customer trust in the process but also lost the order information and suffered a sales loss.
Data loss due to hardware malfunction and cyber attacks are very common. If you lose your data, you lose it for good.
Your only ray of hope is a regular backup. Backup is very much like an insurance token. Regularly keeping your data updated may not help you every day. But in cases like this, it can be a life-saver.
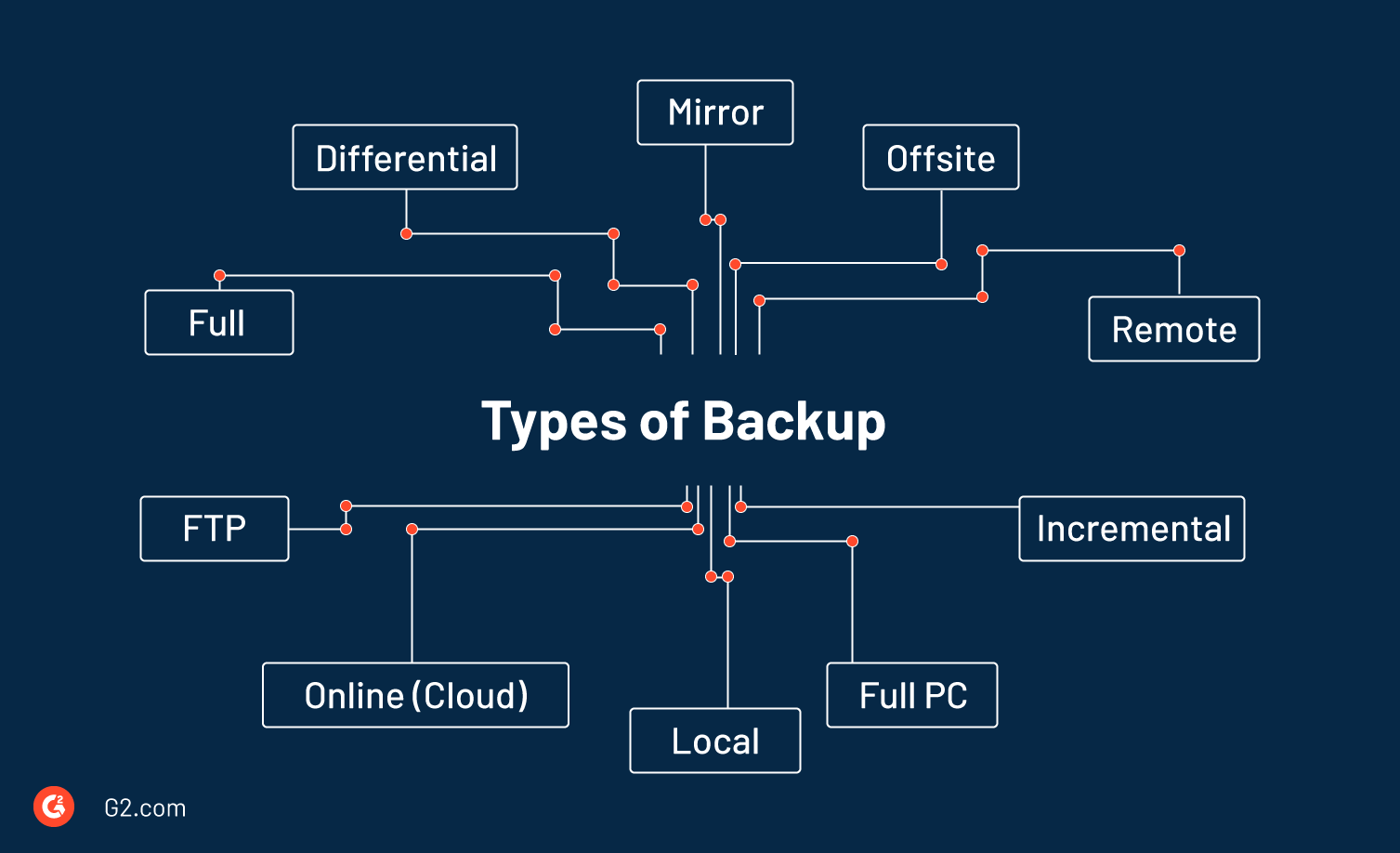
With a backup, you can restore your data and focus on your business while further ensuring better security in the future.
And you don’t have to do much. By opting for an eCommerce web hosting service, you can enable automatic back-up instead of manually backing up your data.
If you want to go above and beyond, make a copy of the backup. In case of an unfortunate circumstance where you lose your original backup, you have a contingency plan available.
8. Never Store Credit Card Data
As an online store, most of your customers are going to opt for card-based payments. To facilitate these payments, a majority of eCommerce stores go for third-party payment gateways.
However, there are some that store their customers’ data in-house. If you’re doing so, you need to know that storing your customers’ credit card data invites numerous risks.
Hackers can easily get hold of customers’ credit card information via phishing attacks, spoofing, hacking, and skimming. The card numbers are stolen from unsecured websites or via identity theft schemes. And these fraudulent activities often go unnoticed until the card incurs unauthorized charges.
The solution is to never store credit card data. Some of the top reasons for the same are:
- Privilege Abuse by Employees
- SQL Injection Attacks
- Storage Media Exposure
- Limited Security Expertise
- Weak Audit Trail
To ensure the safety of your customers’ information, first, understand what the PCI guidelines are and see if storing the data is really necessary. If it is, take it upon yourself to regularly update your software, have customers sign an agreement, and exercise caution for handling sensitive data.
If not, you can simply opt for a third-party payment processor like Stripe that complies with the PCI guidelines and follows the payment protocols for online transactions. They often have the expertise in following the security measures and can reduce your compliance burden.
9. Use a Card Processor with Address and Card Verification
While making digital payments, it’s impossible to verify if the person making the payment is the actual cardholder. To determine the authenticity of the transaction, you need to add extra layers of security. This will reduce credit card fraud.
Apart from the basic details like credit card number and cardholder name, ensure that you ask for the following details
CVV (Card Verification Value): The last three digits on the back of the credit/debit card.
AVS (Address Verification System): A numerical address verification system that determines the match of the address that the customer has with the bank and the address in customer information.
AVS is increasingly used to legitimate online transactions. The merchant automatically sends a request for user verification to the card issuer using the billing address information provided by the consumer. The processor checks the billing address and matches it with the issuing bank.
In case the addresses don’t match, the bank deems the transaction as a failure. In case it does match, the bank discloses a response code that describes how closely the address matches.
Asking for numerous verification details from customers may seem like a hassle for them. But doing so can ultimately help you validate their purchases and ensure their security.
10. Set up Fraud Alerts
There’s still a possibility that the security is at risk despite having two-factor authentication and double verification methods.
Have an alert system that notifies you whenever there is a suspicious activity when customers use their cards to make payments.
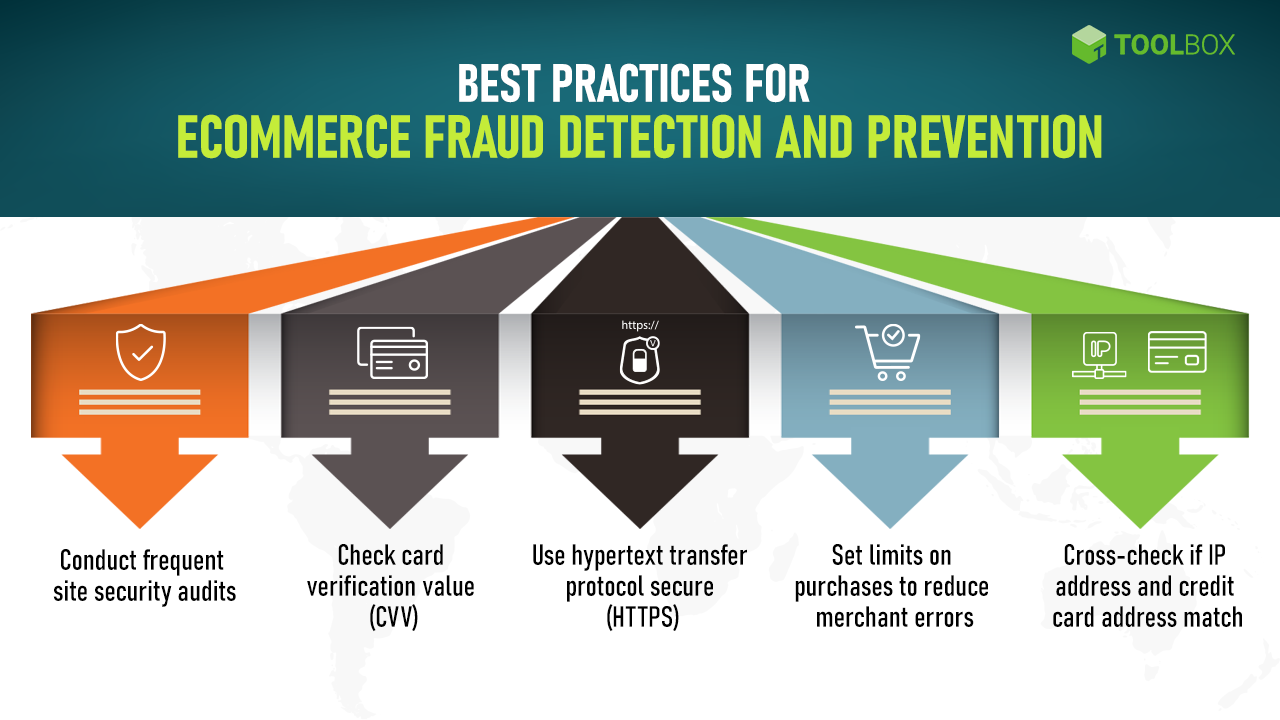
Check your payment processor and set up alerts by using several variables to trigger the alert. These can be:
- Multiple bulk orders are getting paid by a single card
- Orders are placed from a foreign IP address
- Conflicting billing and customer data address
- One person places the same orders using different credit cards
- The zip code on the customer database doesn’t match with the billing information
- Multiple failed payment attempts
In case you receive any of these notifications, you can restrict payments and suspend the order until the above steps are addressed and are manually approved by the actual cardholder.
11. Perform Regular PCI Scans
The PCI rules and regulations have evolved owing to the technological advances and rising number of data breaches.
Following these updates and renewals is the least you can do to maintain your security infrastructure for your eCommerce business.
Most startups and medium-sized businesses don’t invest in data security as they do. Data suggest that more than 50% of the businesses don’t abide by the PCI compliance guidelines. This is a dangerous bargain. It loses you both revenue and customers.
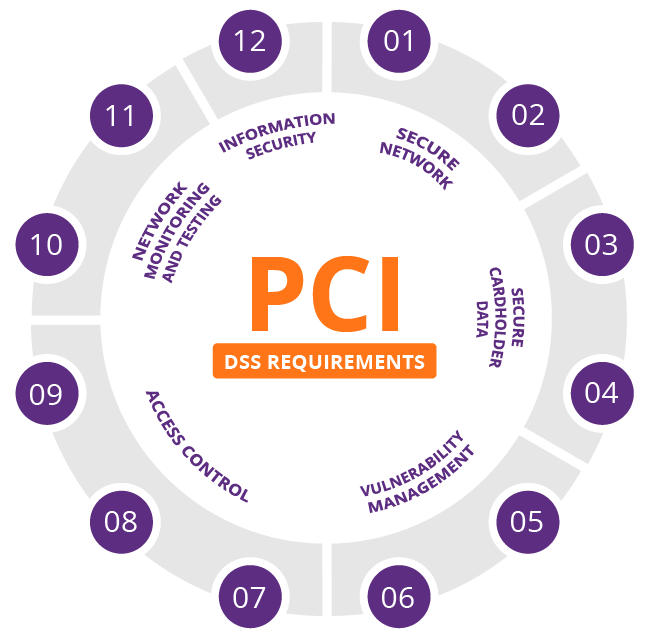
Run PCI scans quarterly to catch issues and maintain the security standard. The basic guidelines that you need to follow are:
- Change the default password for all network devices
- Establish a firewall to safely store credit card information
- Encrypted transmission of customers’ data
- Unique IDs for every cardholder
- Limited physical access to credit card information in the organization
This may take up a few hours every few months. But it can save you thousands of dollars and mitigate security risks for your eCommerce store.
Conclusion
Setting up a security infrastructure is not enough. You’d need to invest your time and efforts and regularly maintain security hygiene that won’t compromise sensitive information and help you keep ahead of your game. Apart from saving your unnecessary costs pertaining to security, it will establish a sense of trust from the customers’ end that can go a long way.







