A Comprehensive Exploration of Magento EAV Model
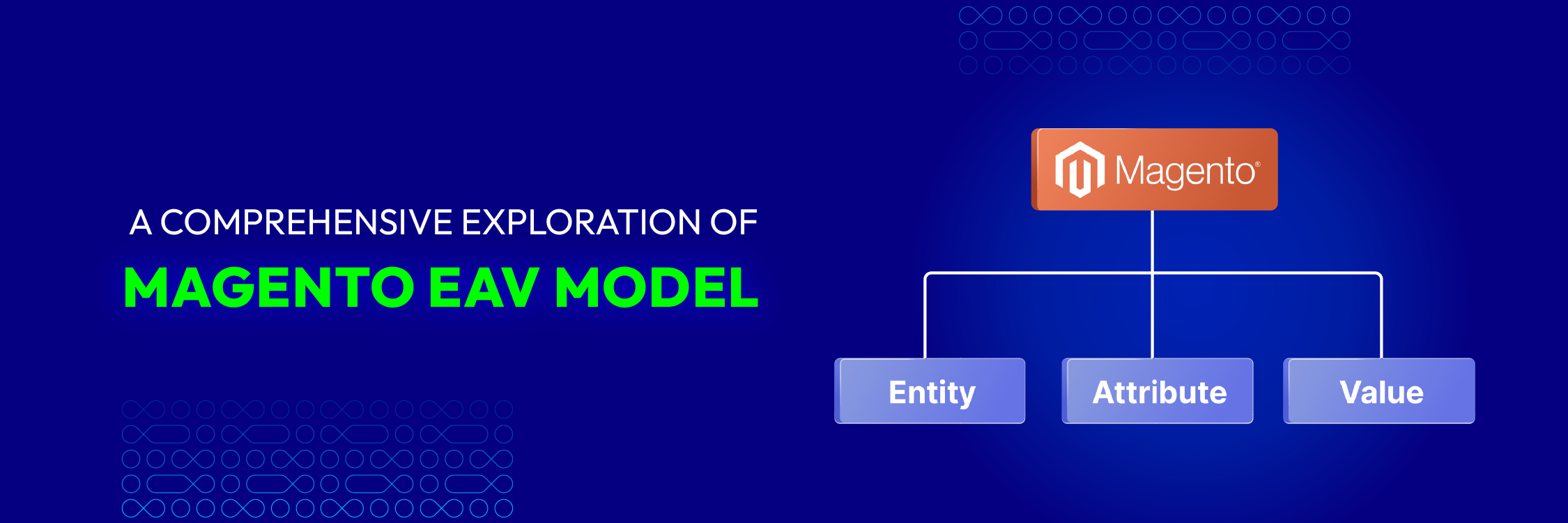
The EAV model in Magento oversees diverse entities and their attributes, offering a versatile framework for organizing product data in your Magento shop. This guide breaks down this crucial aspect, enabling you to adeptly navigate your online store’s database for more effective operations.
What is the Magento EAV Model?
The Magento EAV (Entity Attribute Value) model is a framework that simplifies adding and managing entities and their attributes, with each attribute of an entity stored as a single row in an EAV table.
It serves as a flexible data structure, ideal for entities requiring various attributes to define them, but typically only a limited number of these attributes are relevant for any single entity. This approach enables efficient data management, promoting both adaptability and scalability and is sometimes referred to as the open schema or object attribute value model.
In the EAV setup, each entity has basic information such as its name and function, which are stored in an Objects table. This makes the Magento EAV model an efficient method for organizing the intricate details of items in your online shop, ensuring easy management and retrieval.
Deeper understanding of EAV: Entity, Attribute, and Value
- Entity: In Magento 2, an entity is a term for different kinds of data items, including products, categories, customers and orders; with each type of entity having its own database record.
- Attribute: Data components linked to an entity are called attributes. For example, attributes of the product entity could include its name, price and availability status.
- Value: The term ‘value’ is used to describe the actual data or content that corresponds to a particular attribute.
For example, the entity is product, the attribute is product’s price, and the value is the actual price like $500.
The importance of EAV Model in Magento
The EAV model in Magento plays a crucial role in managing data efficiently, allowing for the seamless addition of new information to your store. Every piece of information contributes to a comprehensive overview of an item, enhancing the customer experience. This model is designed to optimize storage space, but a lack of understanding can complicate the configuration or updating of your online store.
For Magento store developers and operators, familiarity with the EAV model is essential. It organizes and gives form to the site’s data, ensuring seamless integration of various components and maintaining smooth operations.
Entity Table Structure
In the entity-attribute-value (EAV) model, each attribute-value pair is a discrete piece of information about an entity. EAV tables are characterized by their “long” (many rows) and “narrow” (few columns) structure, where data is organized into three main columns.
- The Entity: refers to the item being described.
- The Attribute or parameter: acts as a reference to a definitions table that outlines attributes, containing details such as attribute ID, name, description, and data type. This table might also incorporate columns for input validation like maximum string length, valid format patterns, and allowed values.
- The Value: corresponds to the actual data for the attribute, with each row in the database holding a unique value for an attribute.
How EAV data storage works?
Magento’s approach to managing EAV (Entity-Attribute-Value) data involves a structured separation of data across various tables, enhancing data handling:
- EAV Entity Type: This involves storing the type of each entity along with its model information or the default attribute set.
- EAV Entity: The eav_entity table is designated for storing objects that are linked to a particular entity type.
- EAV Entity Attribute: This structure organizes attributes into groups, with the possibility of multiple attributes per group and attributes being part of several groups. An attribute set defines the total groups, and objects are linked to a specific attribute set.
- EAV Entity Value: To optimize data storage, Magento uses different tables for various data types, such as eav_entity_datetime for dates, eav_entity_varchar for strings, and eav_entity_int for integers.
Creating EAV Attributes in Magento
Method 1: Use Setup Script
To generate a Magento EAV attribute, you can utilize either the InstallData or UpgradeData setup files. Below is an example of how to establish the attribute through InstallData, by including a file named: InstallData.php in the Vendor_Module\Setup directory.
namespace Vendor\Module\Setup;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\InstallDataInterface;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleDataSetupInterface;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleContextInterface;
/**
* Class InstallData
* @package Vendor\Module\Setup
*/
class InstallData implements InstallDataInterface
{
/**
* @var \Magento\Eav\Setup\EavSetupFactory
*/
private $eavSetupFactory;
/**
* InstallData constructor.
* @param \Magento\Eav\Setup\EavSetupFactory $eavSetupFactory
*/
public function __construct(\Magento\Eav\Setup\EavSetupFactory $eavSetupFactory)
{
$this->eavSetupFactory = $eavSetupFactory;
}
/**
* @param ModuleDataSetupInterface $setup
* @param ModuleContextInterface $context
*
* @SuppressWarnings(PHPMD.UnusedFormalParameter)
*/
public function install(
ModuleDataSetupInterface $setup,
ModuleContextInterface $context
) {
$setup->startSetup();
$eavSetup = $this->eavSetupFactory->create();
$eavSetup->addAttribute(
\Magento\Catalog\Model\Product::ENTITY,
'simple_test',
[
'type' => 'text',
'group' => 'Product Details',
'label' => 'Bss Simple Test',
'input' => 'text',
'backend' => '',
'frontend' => '',
'required' => false,
'global' => \Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\ScopedAttributeInterface::SCOPE_GLOBAL,
'is_used_in_grid' => false,
'is_visible_in_grid' => false,
'is_filterable_in_grid' => false,
'visible' => false,
'user_defined' => false,
'searchable' => true,
'filterable' => true,
'comparable' => true,
'filterable_in_search' => true,
'is_html_allowed_on_front' => false,
'used_for_promo_rules' => true,
'visible_on_front' => false,
'used_for_sort_by' => true,
'unique' => false,
'default' => '',
'used_in_product_listing' => true,
'source' => '',
'option' => '',
'sort_order' => 10,
'apply_to' => 'simple,configurable,virtual,bundle,downloadable,grouped'
]
);
$setup->endSetup();
}
}
Method 2: Declarative Schema
In Magento 2.3 and later versions, DataPatch is used to create attributes. For example, you can craft a file for this task:
<?php
namespace Vendor\Module\Setup\Patch\Data;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleDataSetupInterface;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\Patch\DataPatchInterface;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\Patch\PatchVersionInterface;
use Magento\Eav\Setup\EavSetup;
use Magento\Eav\Setup\EavSetupFactory;
/**
* Class ApplyNewAttribute
* @package Vendor\Module\Setup\Patch\Data
*/
class ApplyNewAttribute implements DataPatchInterface, PatchVersionInterface
{
/**
* @var ModuleDataSetupInterface
*/
private $moduleDataSetup;
/**
* @var EavSetupFactory
*/
private $eavSetupFactory;
/**
* ApplyNewAttribute constructor.
*
* @param ModuleDataSetupInterface $moduleDataSetup
* @param EavSetupFactory $eavSetupFactory
*/
public function __construct(
ModuleDataSetupInterface $moduleDataSetup,
EavSetupFactory $eavSetupFactory
) {
$this->moduleDataSetup = $moduleDataSetup;
$this->eavSetupFactory = $eavSetupFactory;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
* @SuppressWarnings(PHPMD.ExcessiveMethodLength)
*/
public function apply()
{
/** @var EavSetup $eavSetup */
$eavSetup = $this->eavSetupFactory->create(['setup' => $this->moduleDataSetup]);
$eavSetup->addAttribute(
\Magento\Catalog\Model\Product::ENTITY,
/**
Add your attribute here.
*/
..........
);
$setup->endSetup();
}
}
How EAV Model works in Magento?
The Magento EAV model works by optimizing and storing attribute values in a dedicated data structure. In this model, EAV tables are used to classify and maintain attribute information. Developers can access and modify these attribute values in Magento collections using SQL queries. The flexibility of the EAV model is based on its ability to accommodate new objects without requiring changes to the database structure, making it easy to modify and extend in Magento.
This flexibility proves beneficial for shop owners and developers, allowing for easier inventory management and flexibility. Essentially, the Magento EAV model provides a structured and scalable way to manage entity assets.
EAV table structure overview
Magento’s EAV table structure is crafted for streamlined data handling, comprising multiple tables that catalog information about entities, attributes, and their corresponding values. Here is a simplified outline of the key elements within the EAV table framework in Magento:
| Table Name | Description |
|---|---|
| eav_entity_type | Store details of various entity types present in the system, such as 'catalog_product' or 'customer_entity' |
| eav_attribute | Hold data on all attributes across entities, covering aspects like attribute code, backend type, and source model |
| eav_attribute_set | Aggregate multiple attributes under a unified label, termed an attribute set |
| eav_attribute_group | Further organize attributes within a set into distinct groups |
| eav_entity | Archive data for entities, like individual products for the 'catalog_product' entity type |
| eav_entity_* (e.g., eav_entity_datetime, eav_entity_decimal, eav_entity_int, eav_entity_text, eav_entity_varchar) | Dedicated tables for storing entity attributes' values, sorted by the value type |
Collectively, these tables form the backbone of Magento’s EAV model, offering a dynamic and efficient framework for data management within Magento platforms. Mastery of this structure is crucial for developers because it allows them to manage information efficiently and customize Magento stores effectively.
Pros and cons of EAV Model
Pros
-
The EAV Model in Magento offers benefits such as flexibility in managing feature redundancy, making it easy to add new objects or attributes without altering the database structure.
-
This flexibility supports increased growth and adaptability while also reducing database storage requirements by only storing relevant attribute values.
-
Attribute control is simplified under the EAV Model, enabling easy updates or removals without disrupting other database components.
-
Additionally, the EAV model supports attribute scope, allowing for specific attribute values to be assigned to different stores or views, enhancing localization efforts and improving the user experience.
Cons
- The EAV model can be complicated and difficult to use and comprehend.
- Query performance might suffer as the model often requires joining several tables, slowing down data retrieval.
- The model’s flexibility in adding attributes without stringent validation can lead to inconsistencies and potential data errors.
- The database footprint can grow significantly due to the EAV model’s structure, necessitating more storage space.
- Effective indexing can be more complicated with the EAV model, potentially impacting the database’s ability to efficiently execute queries.
- The dispersion of data across numerous tables complicates complex queries and data analysis, making these tasks more arduous.
Flat Model vs EAV Model
The EAV Model in Magento is known for its flexibility and dynamic data structure, while the Flat Model excels in performance speed.
| Parameter | Flat Model | EAV Model |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Uses one table to store data. | Uses various tables to store data. |
| Adding Attributes | Needs to change the database schema setup to add new details. | Allows adding new details without altering the database schema. |
| Performance | Faster when loading data collections due to simpler design. | Slower because multiple connections are needed when loading collections. |
| Data Handling | Managing attributes might be hard due to a rigid setup. | Easy to manage and update attributes. |
Although the EAV Model may have performance limitations, it is preferred in Magento for its adaptability and structured data storage.
EAV Model vs Relational Model
Contrasting Magento’s EAV and relational models helps grasp their distinct benefits and when each is most useful. Below is a structured analysis of their main disparities:
Thus, this comparison serves as a roadmap for the selection of sampling models tailored to meet the needs and criteria of specific projects.
| EAV Model | Relational Model | |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Each attribute-value pair represents a fact describing an entity in the EAV model. | The relational model employs a flat table structure and is the conventional form of a keyed relational DB. |
| Flexibility | The EAV model is adaptable to meet changing project requirements. | The relational model may lack adaptability when a project needs change. |
| Efficiency | Suited for scenarios with numerous attributes and varying values due to its flexible structure. | More efficient for scenarios with few attributes and fixed values because of its simple structure. |
| Data Retrieval | May be complex and slow due to the need for multiple joins. | Simpler and faster because of the straightforward flat table structure. |
FAQs
1. How does the EAV structure integrate with Magento?
Within Magento’s normalized database structure, EAV assigns each attribute (e.g., name or SKU) a data type, which then becomes a column in the database table. It also stores the attribute values for each store view.
2. Can custom attributes be added to Magento product pages?
Indeed, developers have the capability to add custom attributes, akin to extensions, to product pages using Magento’s data configuration settings. These attributes are specific to each entity and store view.
3. Where are these newly added attributes stored within the system?
Upon adding an attribute, whether it’s user-defined or set as a default value, it is stored in tables created for each attribute, constituting part of the EAV database structure.
4. What are the two attribute types involved?
The primary types discussed here are ‘static’, where all information resides within the same table, and ‘EAV’, which allocates dedicated storage for potentially extensive unique data, while maintaining relatively compact core entity records.
5. Are there any issues associated with Magento’s EAV model?
Although the EAV model offers flexibility and depth, it could result in complex SQL queries due to multiple joined tables, potentially impacting system performance.
6. How does Magento hosting influence EAV model performance?
Magento hosting significantly impacts the efficiency of the EAV model. A robust hosting solution is essential for handling the complex SQL queries and multiple tables join inherent in the EAV structure, ensuring smooth and swift data retrieval.
Final Thought
Understanding how the Magento EAV Model works is crucial for both store owners and developers. It allows for flexible management of product attributes and makes efficient use of database resources. With its easy attribute addition and modification, the EAV model empowers users to customize their online stores effectively. Selecting a dependable Magento auto-scaling hosting provider is essential for ensuring optimal performance and seamless store operation.





